
As one of the world’s largest economies, Germany’s trade relationships are crucial to its economic stability and growth. In 2024, Germany continued to maintain robust trade activities, with significant partnerships both within Europe and globally. This blog explores Germany’s top trading partners, providing insights into export and import dynamics.
 Top Export Partners
Top Export Partners
- United States
- Value: $170.8 billion
- Percentage of Total Exports: 10.1%
- The United States remains the largest recipient of German goods, with key exports including motor vehicles, machinery, and chemicals
- France
- Value: $125.8 billion
- Percentage of Total Exports: 7.4%
- France is a significant export partner, receiving machinery, automotive parts, and electronic products from Germany.
- Netherlands
- Value: $119.1 billion
- Percentage of Total Exports: 7.1%
- The Netherlands imports a variety of goods from Germany, primarily chemical products, machinery, and motor vehicles.
- China
- Value: $105.3 billion
- Percentage of Total Exports: 6.2%
- Despite a slight decline in trade, China remains a vital export market for Germany, importing automotive products, machinery, and chemicals.
- Poland
- Value: $96.4 billion
- Percentage of Total Exports: 5.7%
- Germany exports machinery, vehicles, and electronic equipment to Poland.
 Top Import Partners
Top Import Partners
- China
- Value: $154 billion
- Percentage of Total Imports: 12.8%
- China is Germany’s leading import source, supplying electronics, machinery, and textiles, contributing to a substantial trade deficit.
- Netherlands
- Value: $153 billion
- Percentage of Total Imports: 12.2%
- The Netherlands is a major supplier of crude oil, machinery, and chemical products to Germany.
- United States
- Value: $148 billion
- Percentage of Total Imports: 12.0%
- The U.S. provides Germany with pharmaceutical products, automotive components, and technology-related goods.
- Poland
- Value: $137 billion
- Percentage of Total Imports: 11.2%
- Poland exports automotive parts, machinery, and agricultural products to Germany.
- Italy
- Value: $125 billion
- Percentage of Total Imports: 10.4%
- Italy’s exports to Germany include machinery, automotive components, and food products.
Trade Deficits and Surpluses
Germany’s trade balance reflects its economic strengths and challenges. Overall, Germany has achieved a significant trade surplus of approximately $226.6 billion, driven by high exports in sectors such as automotive, machinery, and chemicals. Key contributors to this surplus include the United States ($71.3 billion surplus), France ($51.5 billion surplus), and the United Kingdom ($44.9 billion surplus). However, Germany also faces notable trade deficits, particularly with countries from which it imports essential raw materials, electronics, and energy products. Major deficits include China ($63 billion deficit), the Netherlands ($17 billion deficit), and Russia ($7 billion deficit).
Continental Trade Distribution
Germany’s trade spans multiple continents, reflecting its global economic ties. About 54.3% of Germany’s exports go to European countries, and 51.2% of Germany’s imports come from Europe. Approximately 18.9% of German exports are directed to North America, while imports from North America constitute 14.3% of Germany’s total imports. Around 16.8% of Germany’s exports are to Asian countries, with imports from Asia accounting for 20.5% of Germany’s total. This distribution highlights Germany’s integrated role in global trade networks, leveraging its economic strength across continents.
Emerging Markets and New Partnerships
Emerging markets present new opportunities for German exports, as businesses look to expand their reach. Countries in Africa and Latin America are becoming increasingly important, offering untapped potential for growth and collaboration. Developing new partnerships in these regions can drive future economic prosperity. The expansion into these markets allows Germany to diversify its trade portfolio and reduce dependency on traditional markets.
Sustainable Trade Practices
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in trade practices. Germany leads by example, promoting eco-friendly initiatives and green logistics. By prioritizing sustainable trade, businesses can reduce their environmental impact while maintaining economic growth. This commitment to sustainability is essential for meeting global climate goals and ensures long-term economic resilience.
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements play a crucial role in enhancing trade efficiency. Innovations in logistics, such as AI and blockchain, improve transparency and reduce costs. Germany’s investment in technology ensures it remains competitive in the global market, facilitating smoother and more reliable trade operations. These technological innovations are pivotal in optimizing supply chains and enhancing trade facilitation.
Government Initiatives
The German government supports trade through policies and initiatives that promote international commerce. Trade agreements, subsidies, and regulatory frameworks help businesses thrive in the global marketplace. These efforts are vital for fostering a conducive environment for trade and economic growth. Government initiatives aimed at reducing trade barriers and enhancing market access are crucial for sustaining Germany’s robust trade performance.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
Germany’s multifaceted approach to trade, encompassing robust partnerships, emerging market expansion, sustainability, technological innovation, and supportive government policies, underscores its strategic position in global trade networks. By fostering strong economic ties and embracing modern trade practices, Germany not only ensures its economic resilience but also contributes significantly to the global trade ecosystem. For industry professionals, understanding these dynamics offers a wealth of opportunities for strategic planning and growth. Leveraging these insights will be crucial as businesses navigate the evolving landscape of global trade.




 Top Export Partners
Top Export Partners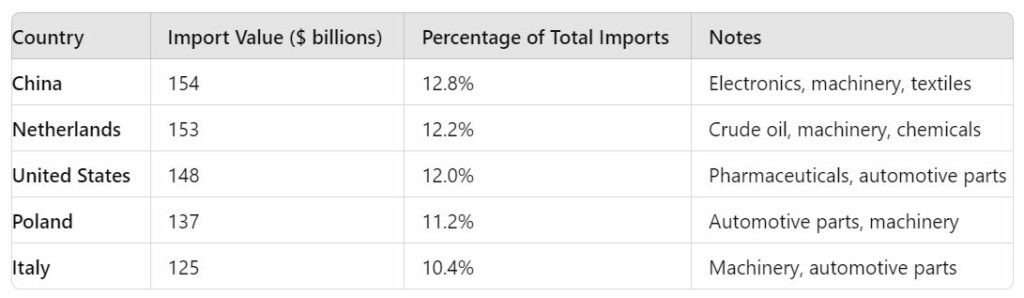 Top Import Partners
Top Import Partners
 Conclusion
Conclusion



