
India’s trade relations with the world are a testament to its robust economic presence and strategic partnerships. From bustling markets in New York to the vibrant bazaars of Beijing, India’s trade footprint is vast and varied. This post will explore India’s top trading partners, highlighting the intricate web of exports and imports that sustain its economy. We’ll also discuss the significance of these relationships for freight forwarding companies, logistics providers, importers and exporters, customs brokers, manufacturers, e-commerce businesses, and industry-related logistics vendors. The insights provided here will help you better understand the dynamics of India’s trade network and how it impacts your business operations.
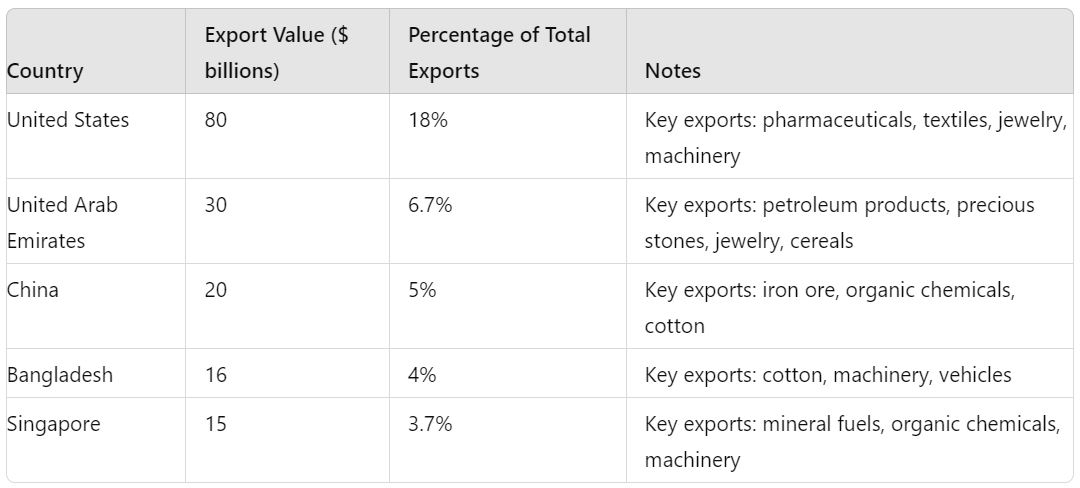
 India’s Top Export Partners
India’s Top Export Partners
- United States
- Value: $80 billion
- Percentage of Total Exports: 18%
- The United States is the largest recipient of Indian exports, with key exports including pharmaceuticals, textiles, jewelry, and machinery.
- United Arab Emirates
- Value: $30 billion
- Percentage of Total Exports: 6.7%
- India exports a diverse range of goods to the UAE, such as petroleum products, precious stones, jewelry, and cereals.
- China
- Value: $20 billion
- Percentage of Total Exports: 5%
- Key exports to China include iron ore, organic chemicals, and cotton, contributing significantly to the trade balance.
- Bangladesh
- Value: $16 billion
- Percentage of Total Exports: 4%
- Major exports to Bangladesh consist of cotton, machinery, and vehicles, reflecting the strong bilateral trade relations.
- Singapore
- Value: $15 billion
- Percentage of Total Exports: 3.7%
- India’s exports to Singapore include mineral fuels, organic chemicals, and machinery, highlighting the strategic economic partnership.
 India’s Top Import Partners
India’s Top Import Partners
- China
- Value: $90 billion
- Percentage of Total Imports: 16%
- China is India’s largest import partner, supplying electrical machinery, organic chemicals, and plastics, which are crucial for various industries.
- United States
- Value: $35 billion
- Percentage of Total Imports: 7%
- Key imports from the United States include machinery, mineral fuels, and aircraft, reflecting the diverse trade relationship.
- United Arab Emirates
- Value: $30 billion
- Percentage of Total Imports: 6%
- The UAE is a significant source of petroleum and petroleum products, along with precious stones and metals.
- Saudi Arabia
- Value: $25 billion
- Percentage of Total Imports: 5.5%
- Saudi Arabia provides India with crude oil and other petroleum products, essential for energy security.
- Iraq
- Value: $20 billion
- Percentage of Total Imports: 4.5%
- Iraq is a key supplier of crude oil to India, playing a critical role in meeting the country’s energy demands.
 Trade Deficits and Surpluses
Trade Deficits and Surpluses
India’s trade balance reveals both strengths and challenges, with significant surpluses and deficits. The country enjoys notable trade surpluses with the United States ($45 billion), the United Arab Emirates ($15 billion), and Bangladesh ($8 billion). These surpluses are driven by the export of pharmaceuticals, textiles, machinery, and petroleum products. Conversely, India faces substantial trade deficits with China ($70 billion), Saudi Arabia ($20 billion), Iraq ($18 billion), and Switzerland ($12 billion). These deficits are primarily due to the import of electrical machinery, crude oil, and essential commodities, including precious metals and stones from Switzerland. Understanding these trade balances is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate deficits and leverage surpluses for economic growth.
Continental Trade Distribution
A significant portion of India’s trade is concentrated within Asia, with approximately 40% of exports and 45% of imports involving Asian countries. This regional focus highlights the strategic economic ties within Asia and the importance of neighboring markets for India’s trade. North America accounts for 23% of exports and 8% of imports, reflecting the strong trade relationship with the United States. Europe plays a crucial role in India’s trade, comprising 17% of exports and 10% of imports, showcasing the diverse trade network with European countries. Africa, Oceania, and South America represent smaller but important trade partners, contributing to the diverse and integrated trade network. This continental trade distribution underscores India’s role as a key player in global trade networks.
Emerging Markets and New Partnerships
India’s trade dynamics are not limited to established partners; emerging markets and new partnerships are becoming increasingly significant. Countries in Africa, Latin America, and Southeast Asia offer new opportunities for trade expansion and diversification. By exploring these emerging markets, India can reduce its dependency on traditional partners and tap into new growth avenues. Establishing trade agreements and partnerships with countries in these regions can enhance market access and create mutually beneficial trade relations.
 Sustainable Trade Practices
Sustainable Trade Practices
Sustainability is becoming a critical aspect of global trade, and India is no exception. Adopting sustainable trade practices can help India align with global environmental standards and contribute to long-term economic stability. This includes promoting environmentally friendly products, reducing carbon footprints in trade processes, and ensuring fair trade practices. By integrating sustainability into its trade policies, India can enhance its global reputation and attract environmentally conscious trading partners.
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements are reshaping the landscape of global trade, and India is leveraging these innovations to enhance its trade capabilities. The use of blockchain technology, artificial intelligence, and IoT in supply chain management can improve transparency, efficiency, and security in trade processes. Digital platforms and e-commerce are also playing a significant role in facilitating international trade, providing new avenues for businesses to reach global markets. By adopting and integrating these technological innovations, India can strengthen its position in the global trade ecosystem.
Government Initiatives
The Indian government is actively supporting the country’s trade growth through various initiatives and policies. Programs such as Make in India, Digital India, and Start-up India aim to boost manufacturing, digital infrastructure, and entrepreneurship, respectively. These initiatives create a conducive environment for trade and investment, fostering economic growth and competitiveness. Government support in the form of trade agreements, export incentives, and infrastructure development further enhances India’s trade potential. By leveraging these government initiatives, businesses can capitalize on new opportunities and expand their global footprint.
Conclusion
India’s trade network is a dynamic web of relationships driving the country’s economic growth and global presence. By understanding key export and import partners, trade balances, continental distribution, and emerging markets, businesses can make informed decisions and strategically position themselves globally. Emphasizing sustainable trade practices, technological innovations, and government initiatives enhances India’s trade capabilities and provides a competitive edge. For freight forwarders, logistics providers, importers, exporters, customs brokers, manufacturers, e-commerce businesses, and logistics vendors, staying updated on these trends and leveraging insights can lead to successful trade operations and growth opportunities. Explore India’s trade network and integrate these insights into your business strategy.




 India’s Top Export Partners
India’s Top Export Partners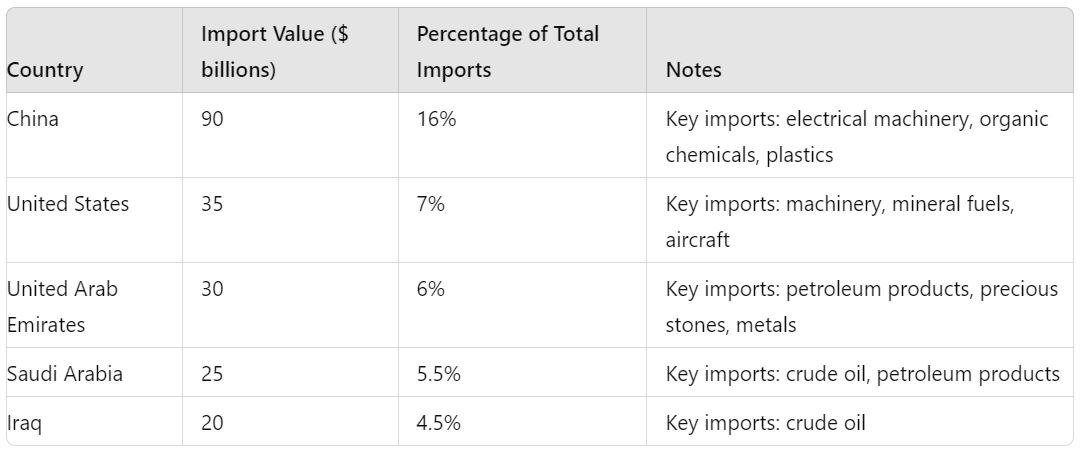 India’s Top Import Partners
India’s Top Import Partners Trade Deficits and Surpluses
Trade Deficits and Surpluses Sustainable Trade Practices
Sustainable Trade Practices



